| Integral of Trigonometric Functions |
Nov. 30, 2024, 3:59 p.m.
Definition
Integration of Trigonometric Functions
-> this refers to the antiderivative of trigonometric functions.
Formulas of Integral of Trigonometric Functions |
1. Sine Integral
-> this states the integral of sine is equal to negative cosine.
Formula:
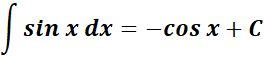
2. Cosine Integral
-> this states the integral of cosine is equal to positive sine.
Formula:
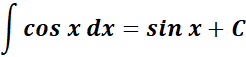
3. Tangent Integral
-> this states the integral of tangent is equal to logarithm secant.
Formula:
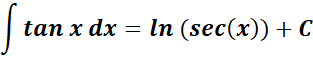
4. Cotangent Integral
-> this states the integral of cotangent is equal to logarithm sine.
Formula:
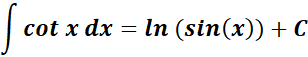
5. Secant Integral
-> this states the integral of secant is equal to logarithm of secant plus tangent.
Formula:
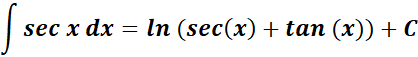
6. Cosecant Integral
-> this states the integral of cosecant is equal to logarithm of cosecant minus cotangent.
Formula:
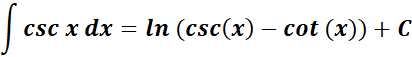
7. Secant2 Integral
-> this states the integral of secant2 is equal to positive tangent.
Formula:
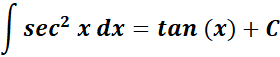
8. Cosecant2 Integral
-> this states the integral of cosecant2 is equal to negative cotangent.
Formula:
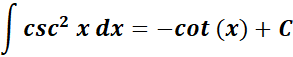
9. Secant - Tangent Integral
-> this states the integral of secant - tangent is equal to positive secant.
Formula:
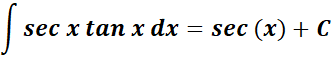
10. Cosecant - Cotangent Integral
-> this states the integral of cosecant - cotangent is equal to negative cosecant.
Formula:
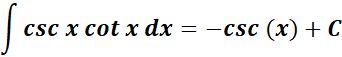
Example |
1. Find the answer from this given:
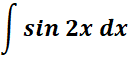
Steps:
a. Write the given 1st.
b. Use the specific trigonometric integral formula.
c. Find the trigonometric integral.
= 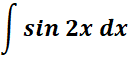
= u = 2x; du = 2 dx; dx = 1/2 du
= Formula: 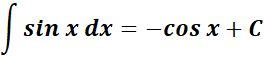
= 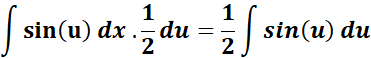
= 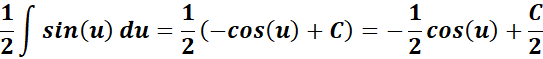
= 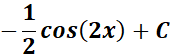
Exercises |
1. 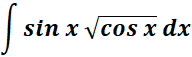
Steps:
a. Write the given 1st.
b. Use the specific trigonometric integral formula.
c. Find the trigonometric integral.
Solution:
= 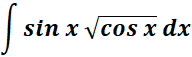
= Formula: 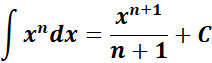
= u = cos (x); du = -sin (x) dx or -du = sin (x) dx
= 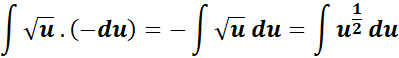
= 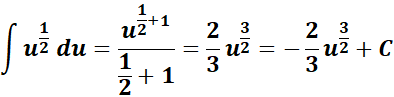
= 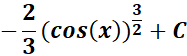
Answer: 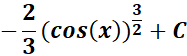
2. 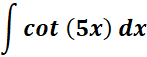
Steps:
a. Write the given 1st.
b. Use the specific trigonometric integral formula.
c. Find the trigonometric integral.
Solution:
= 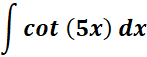
= Formula: 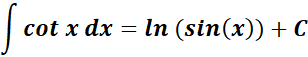
= u = 5x; du = 5 dx; dx = 1/5 du
= 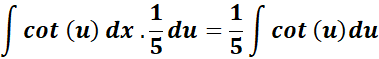
= 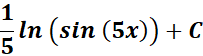
Answer: 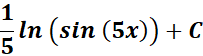
3. 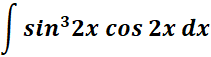
Steps:
a. Write the given 1st.
b. Use the specific trigonometric integral formula.
c. Find the trigonometric integral.
Solution:
= 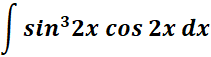
= Formula: 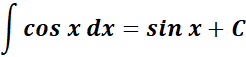
= u = sin (2x); du = 2 cos (2x) dx; dx = du/2 cos (2x)
= Use u and dx to substitute:
= 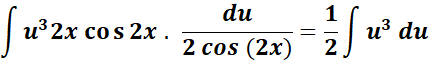
= 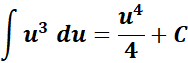
= 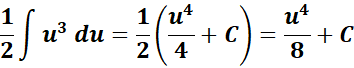
= 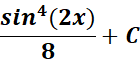
Answer: 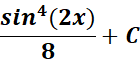
4. 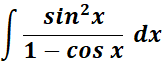
Steps:
a. Write the given 1st.
b. Use the specific trigonometric integral formula.
c. Use trigonometric identity.
d. Find the trigonometric integral.
Solution:
= 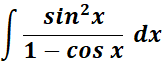
= Formula: 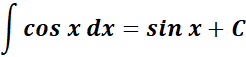
= Use trigonometric identity: sin2 (x) = 1 - cos2 (x)
= sin2 (x) = (1 + cos(x)) (1 - cos (x))
= 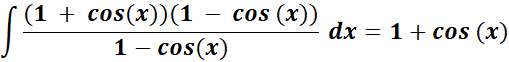
= 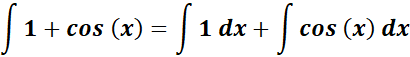
= ![]()
Answer: ![]()
5. 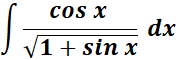
Steps:
a. Write the given 1st.
b. Use the specific trigonometric integral formula.
c. Find the trigonometric integral.
Solution:
= 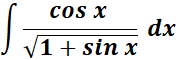
= Formula: 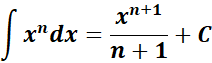
= u = 1 + sin (x); du = cos (x) dx
= 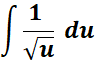
= 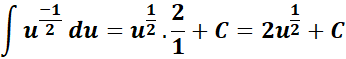
= ![]()
Answer: ![]()
